This post offers a comprehensive guide to the fundamental aspects, functions, and significance of warehousing in today’s global supply chain landscape. From its pivotal role in storing goods to its intricate functions in inventory management, order fulfillment, and beyond, this guide delves into the core principles and diverse types of warehouses. Exploring its impact on business operations, logistics, and customer satisfaction, this comprehensive overview serves as an essential resource for understanding the critical role warehousing plays in the efficient movement and storage of goods, ensuring seamless operations within the supply chain.
What is warehousing?

Warehousing refers to the process of storing goods and products in a designated space, often a building or facility, for a certain period. It involves the management, handling, and organization of inventory within that space. Warehousing serves as a crucial element in the logistics and supply chain process. Allowing businesses to store goods efficiently until they are needed for distribution, sale, or consumption.
What are the types of warehouses?
Warehouses vary in terms of design, function, and the types of goods they store. Here are five common types of warehouses:
Private Warehouses:
- Owned or Leased by a Single Company: These warehouses are solely owned or leased by a specific company to store its own goods. They provide greater control over operations, allowing customization to meet specific storage needs.
Public Warehouses:
- Multi-Client Facilities: Public warehouses offer storage and handling services to various businesses or individuals. These facilities are typically operated by third-party providers and offer space on a rental basis. They provide flexible storage solutions and various services such as inventory management and distribution.
Distribution Centers:
- Focused on Quick Order Fulfillment: Distribution centers are strategically located facilities designed to efficiently distribute products to customers. They specialize in rapidly processing orders, often utilizing modern technology for sorting, picking, and packing to expedite the shipping process.
Cold Storage Warehouses:
- Temperature-Controlled Storage: These warehouses are equipped to store goods requiring specific temperature conditions. Such as perishable goods like frozen or refrigerated products. They maintain controlled temperatures to preserve the quality and safety of the stored items.
Automated Warehouses:
- High-Tech Facilities: These warehouses leverage advanced automation and robotics in their operations. Automated warehouses use technologies such as automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS), conveyor systems. And robotics for tasks like picking, packing, and sorting, enhancing efficiency and reducing human intervention.
These warehouse types cater to different industry needs and goods with specific storage and handling requirements. Businesses choose the type of warehouse that best fits their logistical and operational needs based on factors.
5 important criteria to choose a warehousing solution
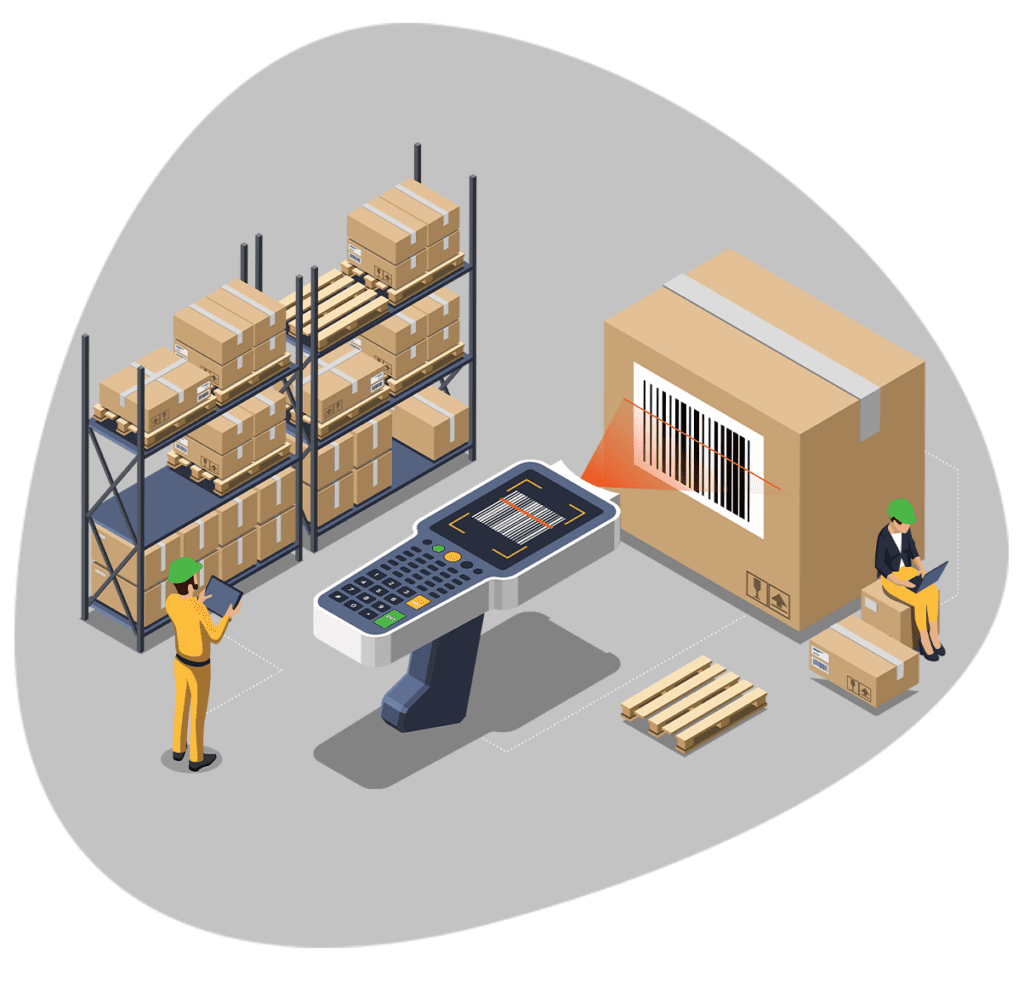

Selecting a warehousing solution is crucial for the smooth operation of your supply chain. Here are five important criteria to consider when choosing a warehousing solution:
Location and Accessibility:
- Proximity to Markets: Choose a warehouse location that is close to your customers or key markets to reduce transportation costs and delivery times.
- Accessibility: Ensure the warehouse is easily accessible by various transportation modes (roads, rail, ports, etc.) for efficient distribution.
Storage Capacity and Flexibility:
- Space Availability: Assess the warehouse’s capacity to accommodate your current inventory needs and potential future growth.
- Scalability: Ensure the warehouse can scale its storage space as your business requirements change, allowing for flexibility without major disruptions.
Technology and Infrastructure:
- Warehouse Management Systems (WMS): Evaluate if the facility uses modern technology and WMS for efficient inventory tracking, management, and order processing.
- Infrastructure: Assess if the warehouse has the necessary equipment, such as handling machinery, racking systems, and technology for seamless operations.
Security and Compliance:
- Security Measures: Ensure the warehouse has robust security measures in place to protect your inventory against theft, damage, or unauthorized access.
- Compliance Standards: Check if the warehouse complies with industry and regulatory standards for safety, quality, and any specific requirements related to your products.
Cost and Service Level Agreements (SLAs):
- Pricing Structure: Evaluate the overall cost, including storage fees, handling charges, and any additional services, to ensure it fits within your budget.
- SLAs: Review the service level agreements, including shipping times, order accuracy, and any additional services provided by the warehouse to meet your business needs.
By assessing these criteria, you can better understand how a warehousing solution aligns with your business objectives and choose the one that best fits your operational requirements and long-term goals.
Warehousing vs. storage
They are related concepts in logistics and inventory management, but they have some distinctions:
Warehousing:
- Function: Warehousing encompasses a broader set of activities beyond mere storage. It involves the systematic and organized handling of goods, including receiving, storing, managing inventory, picking and packing orders, and distributing products when needed.
- Management: Warehousing involves active management of inventory, often using technology and logistics systems to optimize storage space, streamline operations, and efficiently track goods.
- Distribution: Warehousing commonly incorporates a distribution aspect, where goods are organized, packaged, and shipped to customers or other locations.
Storage:
- Function: Storage, on the other hand, primarily refers to the act of holding goods in a physical space for a certain period. It is a part of warehousing but doesn’t encompass the entire set of activities involved in warehousing.
- Duration: Storage can be short-term or long-term and may or may not involve complex management systems or processes beyond stacking and holding goods.
- Focus: While warehousing is more concerned with the efficient flow and management of goods within the supply chain, storage may simply involve holding goods in a space without many additional handling or processing activities.
In essence, warehousing is a more comprehensive and active process that involves multiple functions beyond storage, while storage is a fundamental aspect of warehousing that involves simply holding goods in a designated space. Warehousing typically encompasses a range of logistical and operational activities to manage inventory and facilitate the movement of goods within the supply chain.