
In today’s fast-paced and competitive business landscape, mastering the art and science of stock administration has never been more crucial. It’s a powerful driver of business success, influencing everything from operational efficiency to customer satisfaction and profitability. Inventory control is not merely a process but a strategic tool that, when wielded effectively, can offer a significant competitive edge.
What is Inventory Control?
Inventory control is a critical aspect of successful business operations, ensuring the right balance between stock availability and overstocking. It’s the process of regulating and overseeing the storage, distribution, and ordering of inventory to optimize costs and maintain seamless operations.
The Importance of Inventory Control
Stock administration is pivotal to any business dealing with physical goods. It aids in avoiding stockouts and overstocking, reducing storage and carrying costs, increasing sales and customer satisfaction, and maintaining efficient operations.
Avoiding Stockouts and Overstocking
Inventory control ensures that you have the right amount of stock at the right time. This avoids stockouts, which could lead to lost sales and customer dissatisfaction. Likewise, overstocking can be avoided, minimizing the chances of dead stock and wastage.
Reducing Costs
Effective stock administration reduces storage and carrying costs. It optimizes the use of warehouse space and ensures that resources are not tied up in excess stock.
Increasing Sales and Customer Satisfaction
By avoiding stockouts, stock control can prevent lost sales opportunities and ensure a seamless customer experience. It keeps the stock in sync with demand, ensuring product availability when customers need them.
Key Components of Inventory Control
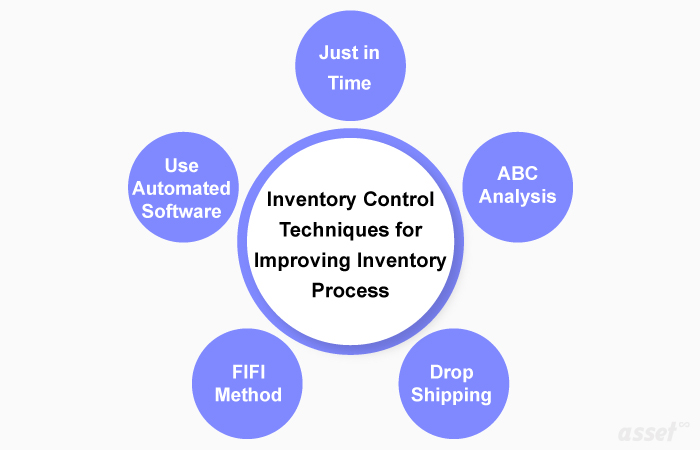
Stock administration comprises several key components, including inventory tracking, demand forecasting, safety stock, reorder points, and ABC analysis.
Stock Tracking
Inventory tracking involves monitoring stock levels and sales. Modern inventory management systems provide real-time updates, enabling prompt reordering decisions.
Demand Forecasting
Demand forecasting involves predicting future sales trends based on historical data and market trends. This helps determine the optimal stock levels.
Safety Stock
Safety stock is the extra inventory kept as a buffer against unexpected demand spikes or supply chain disruptions. This ensures continuous supply even during unforeseen circumstances.
Reorder Points
Reorder points indicate when to reorder a particular item. It’s calculated based on the lead time and the average daily sales.
ABC Analysis
ABC analysis categorizes inventory based on its importance and value. It helps prioritize resources and efforts on the most valuable items.
Implementing Inventory Control: Step by Step
Let’s delve into the step-by-step process of implementing inventory control.
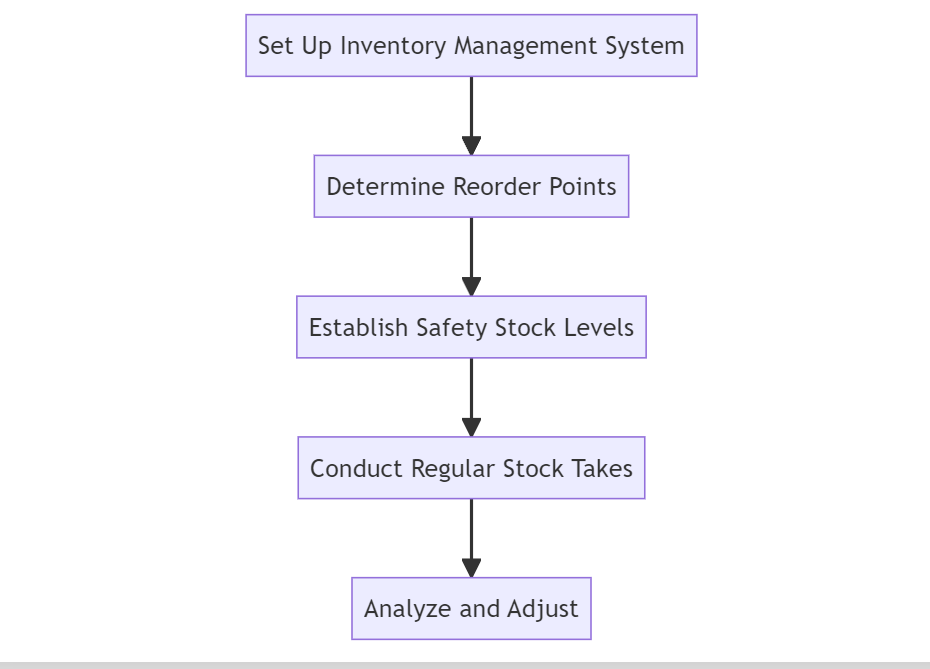
Step 1: Set Up Your Inventory Management System
A robust inventory management system is essential for efficient stock administration. It provides real-time inventory updates and generates useful reports for decision-making.
Step 2: Inventory Control Strategy: Determining Your Reorder Points
Reorder points help avoid stockouts. Calculate it by multiplying your average daily sales by the lead time in days.
Step 3: Establish Your Safety Stock Levels
Determine your safety stock levels based on your business’s risk tolerance and the predictability of demand and supply. The aim is to strike a balance between carrying costs and stockout costs.
Step 4: Inventory Control Excellence through Regular Stock Takes
Regular stock takes help verify the accuracy of your inventory records. It identifies discrepancies, which can then be investigated and rectified.
Step 5: Analyze and Adjust
Regularly analyze your inventory data and adjust your strategies accordingly. This ensures continuous improvement and adaptability.
Embracing Automation in Inventory Control
Automation is a game-changer in stock control. It streamlines processes, improves accuracy, and frees up time for strategic tasks. Automated inventory management systems track inventory in real time, generate alerts for low stock levels, and can even automate reordering processes.
Conclusion
Inventory control is an essential aspect of successful business operations. It optimizes costs, prevents stockouts and overstocking, and ensures customer satisfaction. By implementing a robust stock control system and embracing automation, businesses can significantly enhance their operational efficiency and profitability.
Remember, mastering inventory control is not a one-time activity but an ongoing process of continuous improvement. Keep analyzing, keep adjusting, and keep moving forward!
Understanding the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): A Comprehensive Guide