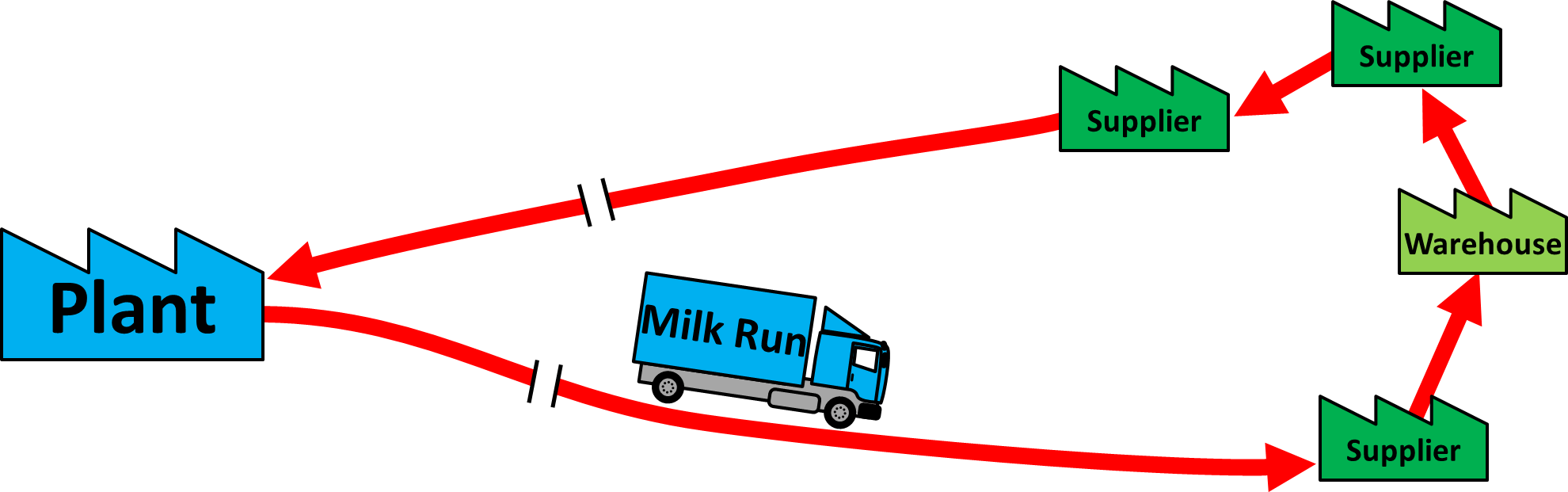
In the intricate world of logistics, where efficiency and optimization are paramount, innovative strategies emerge to streamline operations and reduce costs. One such strategy that has gained prominence is the “Milk Run.” While its name may conjure images of dairy deliveries, the concept of a Milk Run in logistics is far-reaching and impactful. It represents a sophisticated approach to transportation and supply chain management, revolutionizing the way pick up, delivery, and distribute the goods
In our exploration of “Everything You Need To Know About Milk Run in Logistics”. e delve into the core principles, benefits, and applications of this strategic approach
What Is A Milk Run in Logistics?
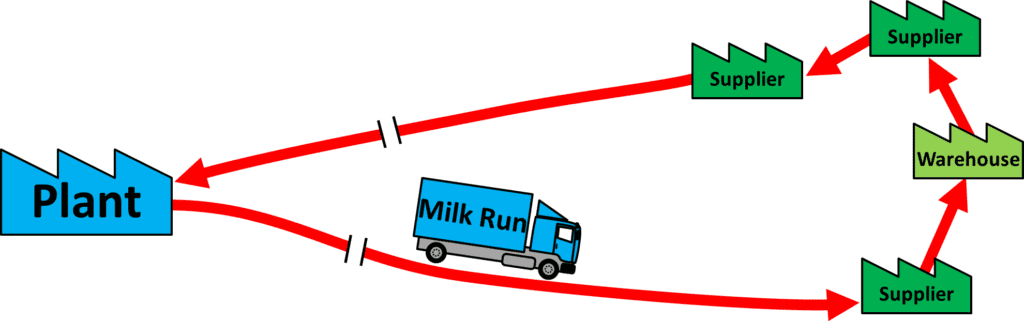
A “Milk Run” in logistics refers to a transportation and supply chain strategy that involves picking up or delivering multiple goods or materials from different suppliers or locations in a single trip.
The primary purpose of a Milk Run is to improve efficiency, reduce transportation costs, and streamline the logistics process by consolidating shipments.
Why is it called a milk run?
The term “Milk Run” in logistics draws its origin from the concept of a milkman’s daily route for delivering milk to households. In the past, before the advent of refrigeration and widespread supermarket distribution, milkmen typically delivery directly milk to homes. These milkmen followed set routes, making regular stops at various households to deliver fresh milk.
The term “Milk Run” was later adopted in the logistics context to describe a similar concept applied to transportation and supply chain operations. In this context, involves a predefined route where a single vehicle picks up or delivers goods from multiple suppliers or customers along the way. The parallel with the milkman’s route lies in the idea of making scheduled stops at different locations to consolidate deliveries or pickups into a single trip
Advantages and disadvantages of milk run logistics

Milk run logistics, as a supply chain strategy, comes with its set of advantages and disadvantages. Here’s an overview:
Advantages
- Efficiency: One of the primary advantages of a milk run is increase operational efficiency. By consolidating pickups or deliveries along a predetermined route. Businesses can reduce travel distances, minimize idle time, and optimize resource utilization.
- Cost Savings: Milk run logistics can lead to significant cost savings. Fewer trips, reduced fuel consumption, and better utilization of transportation assets contribute to lower transportation costs.
- Improved Predictability: The scheduled nature of milk run routes provides a high degree of predictability for both suppliers and customers. This predictability aids in better planning and reduces the chances of disruptions.
- Just-In-Time (JIT) Practices: Milk runs facilitate JIT inventory practices by allowing suppliers to deliver smaller quantities more frequently. This reduces the need for large inventory stockpiles and supports smoother production processes.
- Reduced Lead Times: Consolidating shipments and optimizing routes often leads to reduced lead times. Faster deliveries contribute to improved customer satisfaction and increased responsiveness to demand fluctuations.
- Environmental Impact: With fewer vehicles on the road and minimized travel distances. ilk run logistics can help reduce carbon emissions and contribute to a more environmentally-friendly approach.
Disadvantages
- Complex Planning: Designing and managing milk run routes can be complex, especially when dealing with multiple suppliers, locations, and delivery schedules. Effective route planning requires careful coordination.
- Dependency on Schedule: A milk run’s success depends on adhering to the planned schedule. Delays at one stop can have a cascading effect on subsequent stops, potentially leading to disruptions.
- Limited Flexibility: The fixed routes and schedules of milk runs can limit the flexibility to accommodate sudden changes or urgent requirements. Businesses need contingency plans for unexpected situations.
- Initial Investment: Implementing a milk run strategy may require an initial investment in route optimization software, training, and potential adjustments to existing logistics processes.
- Risk of Over-Complication: In some cases, attempting to incorporate too many stops or locations in a single milk run route can lead to over-complication and reduced effectiveness.
- Dependency on Volume: Milk run logistics may be most beneficial when there’s a sufficient volume of goods to consolidate.
In summary, offers substantial benefits in terms of efficiency, cost savings, and improved predictability. However, it also requires careful planning, adherence to schedules, and consideration of the potential drawbacks. Implementing a milk run strategy should be based on a thorough assessment of the specific needs and characteristics of the supply chain and business operations
What is the role of milk run in lean manufacturing?
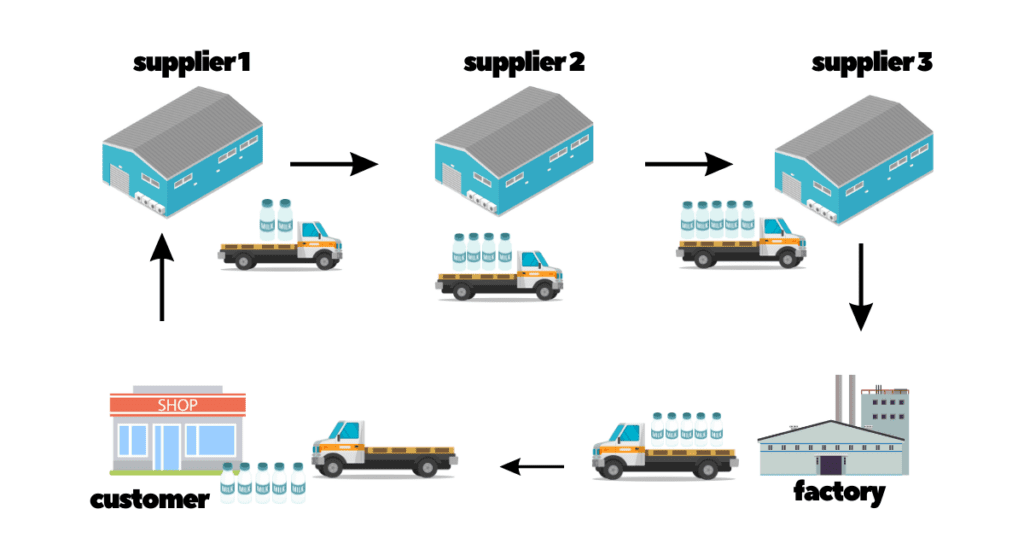
Here’s how a milk run contributes to lean manufacturing:
Waste Reduction
Lean manufacturing aims to eliminate all forms of waste from the production process. It aligns with this principle by minimizing transportation waste. It ensures that delivery materials precisely when needed, reducing the need for excess inventory storage, overproduction, and unnecessary handling.
Just-in-Time Production
It supports JIT production by delivering materials and components in sync with production schedules. This reduces the need for large inventory stockpiles and allows manufacturers to produce what is needed when it’s needed, thereby minimizing waste and improving flow.
Optimized Transportation
Lean manufacturing seeks to optimize all processes, including transportation. A milk run’s predefined route and scheduled stops help optimize transportation routes, reducing travel distance, and improving resource utilization.
Reduced Lead Times
Milk runs enable timely delivery of materials and components to the production line. This reduces lead times, improves production flow, and allows for quicker response to changes in demand.
Flexibility and Adaptability
In lean manufacturing, flexibility is crucial to quickly adapt to changes in demand or production requirements. A well-designed milk run route can incorporate flexibility to accommodate changes while maintaining the core lean principles.
Visibility and Communication
Effective communication and visibility are vital in lean environments. A strategy often involves real-time tracking and monitoring of deliveries, providing transparency into material movements and supporting better communication between suppliers and manufacturers.
Batch Size Reduction
Lean manufacturing encourages smaller batch sizes to minimize the risk of producing excess inventory. It supports this approach by delivering smaller quantities more frequently, aligning with the production needs.
Continuous Improvement
Lean manufacturing thrives on the concept of continuous improvement. A milk run strategy can be refined and optimized over time to further enhance efficiency, reduce waste, and respond to changing production requirements.
Standardization
Lean manufacturing emphasizes standardized processes to reduce variation and improve consistency. A milk run’s predefined routes and schedules contribute to standardization in material handling and transportation.
Labor Efficiency
It can optimize labor resources by minimizing the time spent on transportation and handling activities. This allows workers to focus on value-added tasks within the production process.