
In the fast-paced world of business and manufacturing, understanding lead time is essential for success. Whether you’re a seasoned industry professional or just starting your entrepreneurial journey, comprehending the intricacies of lead time can make or break your operations. This comprehensive guide, we delve deep into the world of lead time, exploring its significance, types, and the profound impact it has on businesses and supply chains. By the end of this journey, you’ll have the knowledge and insights to optimize processes, meet customer demands, and stay ahead in today’s competitive marketplace.
What is lead time?

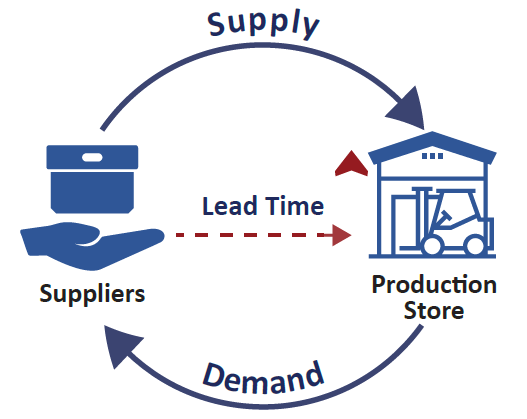
Lead time is the total amount of time it takes for a product or order to move through a specific process, from the initiation or order placement to its completion or delivery to the customer. Lead time includes all the individual stages and activities within the process, such as order processing, production, quality control, transportation. any waiting or delay times that occur between these steps.
What are the types of lead times?
They are the amount of time it takes for a process to be completed, from the initiation to the final delivery. In various industries and contexts, there are different types of lead times, each serving a specific purpose. Here are some common types of lead times:
Manufacturing Lead Time
This is the time it takes to produce a product from the moment a manufacturing order place until the product is ready for shipment. It includes all the processes involved in manufacturing.
Order Lead Time
Order lead time encompasses the time it takes from when a customer places an order until the product delivery to their doorstep. It includes order processing, manufacturing, and shipping.
Supplier Lead Time
Supplier lead time measures the time it takes for a supplier to deliver raw materials or components after receiving an order. It’s critical for production planning and inventory management.
Transportation Lead Time
This is the time it takes for goods to transport from one location to another, considering factors like shipping mode, distance, and transit times.
Replenishment Lead Time
Replenishment lead time refers to the time it takes to restock inventory or reorder products once the existing stock falls below a certain level. It involves the entire procurement process.
These are five fundamental types of lead times that are crucial in supply chain management and production planning. Businesses often focus on optimizing these lead times to improve efficiency and meet customer demands effectively.
Why is it important to avoid long lead times?
Avoiding long lead times is important for several reasons, and it has a significant impact on various aspects of business operations. Here are some key reasons why minimizing lead times is crucial:
Customer Satisfaction
Long lead times can result in delayed product deliveries, which can lead to customer dissatisfaction. Timely deliveries are crucial for meeting customer expectations and maintaining a positive reputation. Customers are more likely to be loyal to businesses that consistently deliver products on time.
Inventory Management
Long lead times often necessitate holding higher levels of inventory to ensure that products are available when needed. Excess inventory ties up capital and storage space, increasing carrying costs. Reducing lead times enables more efficient and cost-effective inventory management.
Market Responsiveness
In today’s rapidly changing business environment, the ability to respond quickly to market trends, customer demands, and competitive pressures is essential. Shorter lead times allow companies to be more agile and responsive to shifts in the market, giving them a competitive advantage.
Cost Efficiency
Long lead times can lead to increased transportation costs, expedited shipping charges, and higher holding costs for inventory. Reducing lead times can lead to cost savings by minimizing these additional expenses and improving resource utilization.
Supply Chain Resilience
Shorter lead times make supply chains more resilient to disruptions, such as natural disasters, supplier issues, or geopolitical events.
Lead time vs. cycle time vs. takt time
Lead time, cycle time, and takt time are all important concepts in manufacturing and process management, and they each serve different purposes. Here’s an explanation of each term:
Lead Time:
- Definition: Lead time is the total time it takes for a product or order to go through a process from initiation to completion. It encompasses all the steps, including waiting time, processing time, and any delays that may occur during the process.
- Purpose: Lead time often use to understand the overall efficiency of a process or supply chain. It helps in setting customer expectations, managing inventory levels, and identifying areas where improvements can be made.
Cycle Time:
- Definition: Cycle time is the time it takes to complete one cycle of a specific task or process. It represents the time required to produce one unit of a product or complete one operation.
- Purpose: Cycle time use for process optimization, capacity planning, and identifying bottlenecks. Reducing cycle time often leads to increased productivity and shorter lead times.
Takt Time:
- Definition: Takt time is the available production time divided by the customer demand rate. It represents the time available to produce one unit to meet customer demand. Takt time is typically expressed in seconds per unit.
- Purpose: Takt time is used to establish a rhythm or cadence in production that aligns with customer demand. It helps balance the production rate with customer needs, ensuring that products are produced at a steady and efficient pace.
These three concepts are essential for improving efficiency, meeting customer requirements, and optimizing processes in manufacturing and other industries.