Backorder, a common occurrence in supply chain management, pose significant challenges for businesses across various industries. When customer demand exceeds available inventory, backorders arise, resulting in delayed order fulfillment and potential dissatisfaction among customers. Understanding the causes, impacts, and effective strategies for managing backorders is crucial for organizations striving to maintain customer satisfaction and maximize operational efficiency. In this post, we will delve into the intricate nature of backorders, exploring the reasons behind their occurrence, the far-reaching impacts on businesses, and the proactive measures that can be implemented to mitigate their adverse effects. By comprehending the complexities of backorders and adopting appropriate strategies, businesses can optimize their supply chain operations and ensure seamless customer experiences.
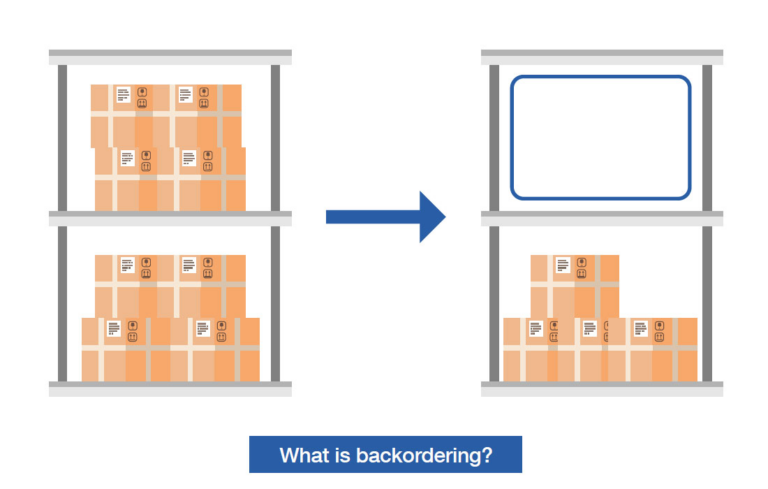
What Is Backorder?

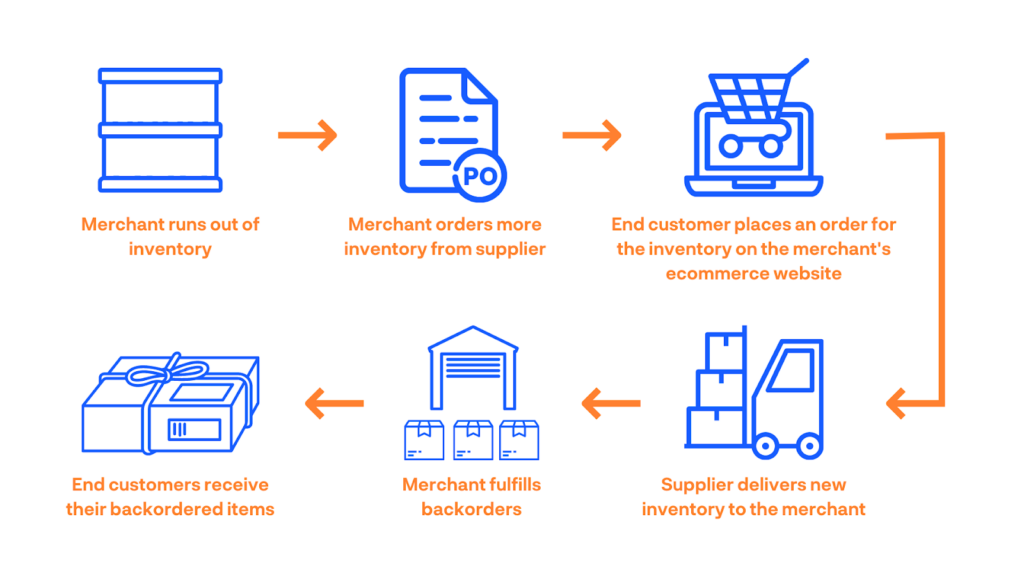
A backorder is a term used in business to describe a situation where a customer places an order for a product or service that is currently out of stock or unavailable. Rather than canceling the order, the company accepts it and records it as a backorder.
When a product is on backorder, it means that the company acknowledges the customer’s request but is unable to immediately fulfill it due to a temporary lack of inventory. The company then prioritizes fulfilling the backorders as soon as the product becomes available again, typically in the order they were received.
Customers who place backorders are typically informed about the situation and provided with an estimated timeframe for when the product is expected to be restocked and their order fulfilled. The length of time for a backorder to be fulfilled can vary depending on the product, company policies, and external factors affecting the availability of the item.
What causes backorders?
Backorders can occur for various reasons, such as unexpected high demand, production delays, supply chain disruptions, or a mismatch between customer demand and inventory levels. It allows customers to secure their place in line for the product they want, even if it’s not currently in stock.
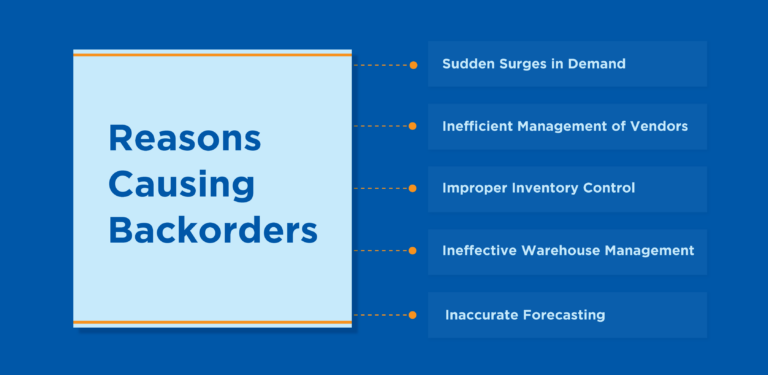
Backorders can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
High demand
When the demand for a product exceeds the available supply, backorders can occur. This can happen due to a sudden surge in popularity, seasonal demand, or unexpected events that increase demand for a particular product.
Supply chain issues
Backorders can arise when there are disruptions or delays in the supply chain. This can include problems with sourcing raw materials, manufacturing delays, transportation issues, or distribution challenges.
Production capacity constraints
If a company’s production capacity is unable to meet the demand for a product, backorders can occur. This can happen when a company experiences increased demand beyond its current production capabilities.
Inventory management
Poor inventory management practices can lead to backorders. This can include inadequate forecasting, inaccurate demand projections, or errors in stock replenishment, resulting in insufficient inventory to fulfill customer orders.
Supplier issues
Backorders can arise when suppliers fail to deliver products on time or provide inadequate quantities. This can be due to supplier production issues, quality problems, or delays in shipping.
Product customization or manufacturing complexity
If a product requires customization or involves complex manufacturing processes, it may be more susceptible to backorders. These factors can lengthen the production time and increase the likelihood of delays.
Unexpected events
Natural disasters, labor strikes, political unrest, or other unforeseen events can disrupt supply chains and lead to backorders. These disruptions can impact manufacturing, transportation, or the availability of raw materials.
Seasonal fluctuations
Some industries experience seasonal fluctuations in demand, such as during holiday seasons or specific times of the year. Companies may struggle to keep up with the demand during peak periods, resulting in backorders.
It’s important to note that backorders are often the result of a combination of factors rather than a single cause. Companies typically strive to minimize backorders by implementing effective supply chain management practices, improving forecasting accuracy, and maintaining appropriate inventory levels.
How long do backorders take?

The duration of backorders can vary significantly depending on several factors, including the specific product or service, the company’s policies and practices, and the circumstances surrounding the backorder.
In general, a backorder occurs when a customer places an order for a product that is temporarily out of stock or unavailable. The company then records the order and prioritizes fulfilling it once the item becomes available again. The time it takes to fulfill a backorder can range from a few days to several weeks or even months, depending on the availability of the product and the company’s ability to restock it.
If the product is in high demand or experiencing production or supply chain issues, the backorder fulfillment time may be longer. Similarly, if the company has a large backlog of backorders or faces logistical challenges, it can further extend the waiting period.
To get accurate information about the specific backorder you’re concerned with, it’s best to contact the company or vendor directly. They should be able to provide you with an estimated timeframe for fulfilling your backorder based on their current circumstances.
Advantages And Disadvantages Of Selling On Backorder
Advantages Of Selling On Backorder
Revenue Generation
Selling on backorder allows you to generate sales and revenue even when you don’t have the product in stock. This can help maintain a steady cash flow and prevent potential loss of sales to competitors.
Customer Retention
By offering backorders, you can retain customers who are willing to wait for the product rather than going to a different seller. This helps maintain customer loyalty and prevents them from seeking alternatives.
Forecasting Demand
Backorders provide valuable insights into customer demand for specific products. By tracking backorder quantities, you can gain a better understanding of which products are popular and adjust your inventory levels accordingly.
Reduced Inventory Risk
By selling on backorder, you can mitigate the risk of overstocking or understocking. It allows you to align your inventory levels with actual customer demand, reducing the chances of inventory obsolescence or stockouts.
Disadvantages Of Selling On Backorder
Customer Dissatisfaction
Customers may become frustrated if they have to wait a long time for their backordered products to be delivered. This can lead to negative reviews, customer complaints, and potential damage to your brand reputation.
Uncertain Delivery Times
When selling on backorder, it can be challenging to provide accurate delivery timelines, especially if you rely on suppliers or manufacturers. This uncertainty can lead to dissatisfaction and may cause customers to cancel their orders.
Fulfillment Challenges
Managing backorders requires careful inventory management and coordination with suppliers. If there are delays or issues in restocking the products, it can further prolong the delivery process and increase the risk of order cancellations.
Cash Flow Constraints
Selling on backorder means accepting payment upfront while delaying product delivery. This can tie up your cash flow, as you may need to refund customers or face challenges in meeting other financial obligations while waiting for restocked inventory.
Overall, selling on backorder can be a strategic approach to manage inventory and generate revenue. However, it requires careful planning, efficient communication with customers, and effective supply chain management to minimize the associated disadvantages and ensure a positive customer experience.